CRUD Application Using Node JS - Part 1 : Introduction on tools, problem statement and configuration
Hello wonderful people! How y'all doing.
I have a desire to learn Node JS for a long time. But due to some situations and busy schedule I am not able to spend some time on learning that. Ohh ohh wait... just kidding. The fact is even I do want to learn, I became so lazy that after my daily work is getting over, I am not in a mood to do anything. So, I just want to fight with my inner-self that is preventing me to do that today. The only way we can get motivation to learning is when there is an external force, deadline or a strong cause for that.
Introduction
For every backend language like Node, Spring Boot etc., one thing is pretty common, the REST API's and CRUD operations. If we get to know how to create them, a concrete idea will be formed on how to work with that particular language.
In this course we are doing the same thing. We are going to learn how to perform CRUD operations in Node JS by using Mongo DB as backend.
Note that this series is purely for very basic understanding and things like best practices, securities etc., which are a little high level concepts are not covered. The only intention is to make the path clear so that you yourself can explore further very easily.
We are not focusing on any client language like Angular or React because its up to you where you want to use the API's. You can use in an Angular application, React application and even for Android application; it doesn't matter.
Tools
There are different ways in which we perform API calls. They are basically GET, POST, PUT, DELETE which are otherwise we imply to as Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) respectively in general.
As I already told I am not going to create any client application for consuming all the API's. So, in order to test our application we will use a tool called Postman which is used to test our REST API's.
You can learn about postman in this video
And we are also going to be using a framework for NodeJS which is ExpressJS which will provide some pre defined functionalities.
And the last thing is Nodemon, which is used to auto refresh the application.
Configuration
There are some softwires that you need to install in order to get started with the NodeJS development.
1. Node
You can download latest LTS version of Node JS from here.
2. Mongo DB
As we are using Mongo DB for storing data as a database, you need to install it in your system. And in this tutorial I am not going to be covering that because there are thousands of tutorials out there in internet. Its a very straightforward process.
3. Problem Statement
Well, for the problem statement, we are not going to build something which we can sell it and earn money! But a very simple app with one entity.
We have a Programmer, who have attributes of Name, Age, Skill and hasJob.
In short
Programmer:
- name (string)
- age (number)
- skill (string)
- hasJob (boolean)
And if we consider our application is running in port 9000, the different API's look like this:
- Saving the programmer details
POST : http://localhost:9000/programmer
- Fetch all the programmer details
GET : http://localhost:9000/programmers
- Fetch a particular programmer with unique ID
GET : http://localhost:9000/programmer/<id>
- Delete a perticular programmer details
DELETE : http://localhost:9000/programmer/<id>
4. VS Code
In this tutorial I am going to use VS code simply because I am used to it. You can use your own anyway.
Starting with basic App
We know what all we need in order to get started. Now, we will create the entry point of our Node JS application that is package.json and app.js*. We need to install packages like ExpressJS and Mongoose for Mongo DB and Nodemon in our application. So, in order to that we need package.json file. And app.js** is basically the entry point of our Node application.
I have created a folder NodeJs and opened the VS Code in that folder. In the terminal, we need to execute one command in order to create package.json. That is npm init. After you run it, it will ask some questions:
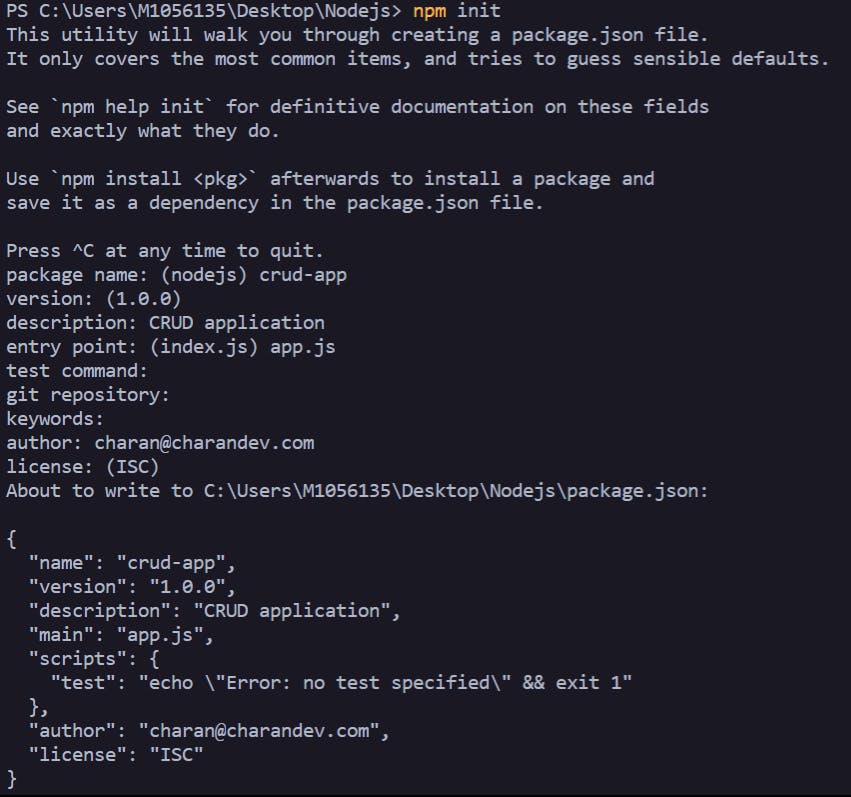
The questions are self explanatory. It looks like the above screenshot. After running that, we can see our package.json file have been created.
Now we will install Express by using the command
npm install express
And similarely, you have to install MongoDB, Mongoose and Nodemon ( for auto reload)
npm install mongodb
npm install mongoose
npm install nodemon
After installing you can see those dependencies are added to package.json:
{
"name": "crud-app",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "CRUD application",
"main": "app.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "charan@charandev.com",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.17.1",
"mongodb": "^3.6.4",
"mongoose": "^5.11.19",
"nodemon": "^2.0.7"
}
}
Now in scripts: section we will need to have one custom script to run start our application, since we are using nodemon to run it, we usually have to write like nodemon app.js. But if we have our custom start script configured, we can use npm start for that.
"scripts": {
"start": "nodemon app.js"
},
Finally, we have to create app.js file as its the entry point of our app. After that the dolder structure will look like:
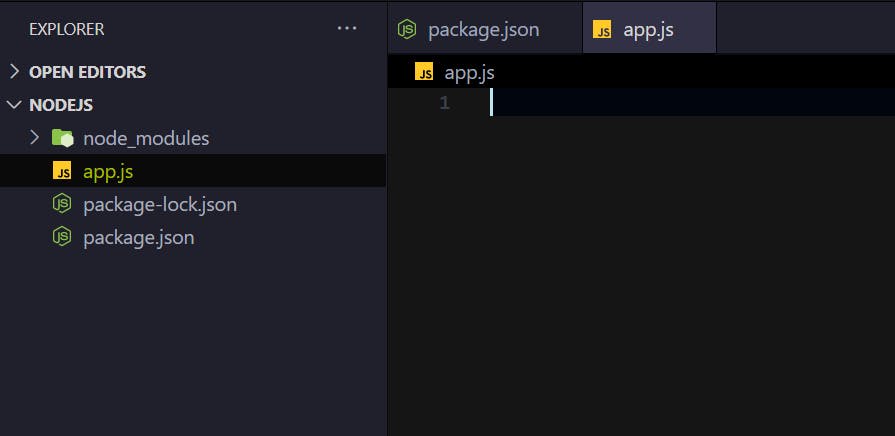
We will wrap up here for our first part of this series. Hope you learned something new today. Keep checking this thread for next parts.

