Hello gorgeous people!
Today's article is about my learning from one of my recently faced problem when I am writing some JavaScript code. I know JavaScript is weird, but that feeling is constantly growing day by day by these kind of behaviors of JavaScript!
Today I am going to explain you about Deep Copy and Shallow Copy in JavaScript.
TL;DR; The definitions of the same are as follows:
Shallow copy
Shallow copy is a bit-wise copy of an object. A new object is created that has an exact copy of the values in the original object. If any of the fields of the object are references to other objects, just the reference addresses are copied i.e., only the memory address is copied.
Deep copy
A deep copy copies all fields, and makes copies of dynamically allocated memory pointed to by the fields. A deep copy occurs when an object is copied along with the objects to which it refers.
Let's understand using an example
To start off, we don't directly move to the actual concept, consider the below code snippet:
let s = 'sai';
let g = s;
s = 'charan';
console.log(s, g);
I have a variable s to which I have assigned a string value of sai. I also declared another variable g and assigned our previously created s to it. In the next line I modified the value of s which is sai previously to a new string charan. In this case, we are only playing with primitive values, meaning - only string values but not any objects or arrays which are non-primitive values.
Now, if we run this:
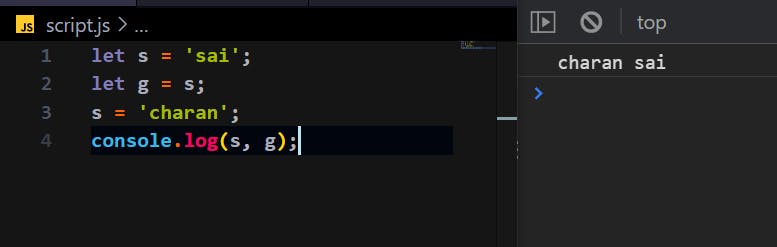
We got the expected result, charan sai. Where the first variable is s which we have changes to a new value and the second one is g in which the data we copied from s before its changed to new value.
Ok. So far so good. Let's climb another step up! Consider we have another variable shallowArr which is an array this time.
let shallowArr = [
123,
'bob',
true,
null,
undefined
];
If you see shallowArr is having primitive values. No complex nested arrays or objects involved, just direct values like Integers, Strings and Booleans.
Now, the way things work in JavaScript is that, most of the times we are dealing with passing values by reference, UNLESS YOU ARE DEALING WITH PRIMITIVES.
That's why in the previous example, we have sai which is assighed to s is a primitive value, and when we did let g = s the primitive value in s is directly copied to g.
Now, if I repeat the same thing with the shallowArr, which is a non-primitive value.
let arr = shallowArr;
shallowArr[0] = 250;
console.log(arr, shallowArr);
Here I tried to copy the shallowArr into another variable arr. And after that at shallowArr[0] = 250, I modified the first value of shallowArr to a new value 250.
Now, if things went same as before, we should get two different arrays like the 0th value in shallowArr should be changed but the 0th value in arr should remain same as before ie., 123.
But if we run it, the result is:
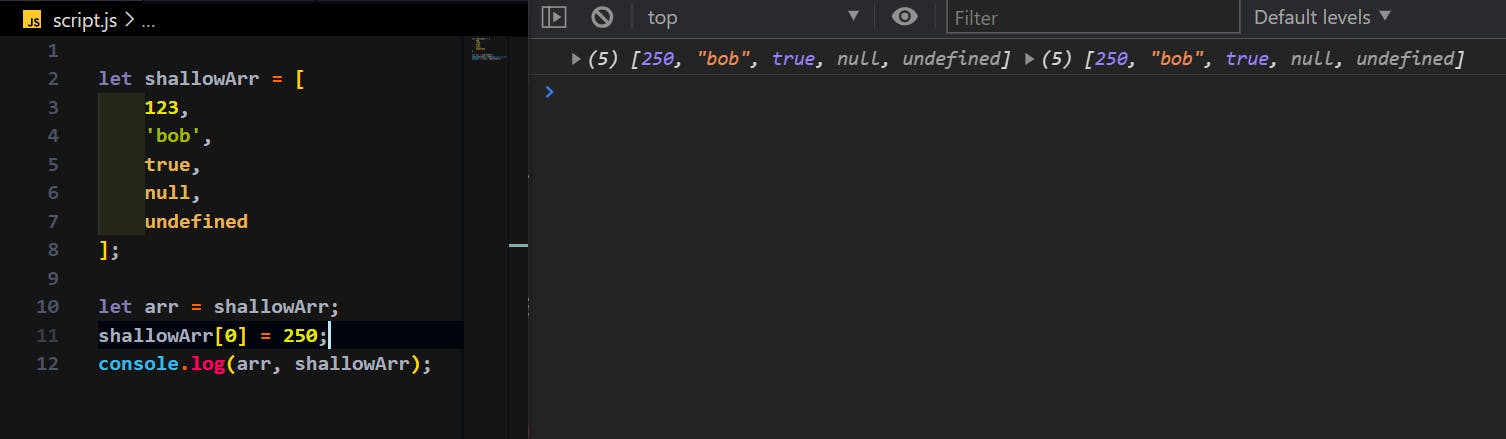
Notice that the output we got seems little different. Even though we have assigned arr with shallowArr before changing the value of its 0th element, we got same value which is a newly changed value of 0th element.
Why this is happened?
Because as I already told you, in the line
let arr = shallowArr, sinceshallowArris not a primitive value, the reference of it is being stored in the variablearr.
So, as arr contains just the reference of shallowArr, whatever the changes we do in shallowArr, it will reflect in arr variable as well.
If we really want to make a new copy of shallowArr, we need to use few methods. And this is what Shallow Copy is.
Shallow Copy
Using shallow copy, we can copy a value which is non-primitive (Array or Object) like shallowArr above and ideally all the values inside that array or object are primitive (we will discuss the reason later).
In order to do Shallow Copying, we have some set of methods:
/*********************
Shallow Copy Method examples
1. arr1.slice(0)
2. [].concat(arr1)
3. Spread Operator
4. Object.create({}, obj)
5. Object.assign({}, obj)
6. Array.from(arr1)
*********************/
Some of which are array methods and some of which are Object methods.
I am not going to explain every method above, but we will use Array.from()
let arr = Array.from(shallowArr);
shallowArr[0] = 456;
console.log(arr, shallowArr);
Now, if we run it:
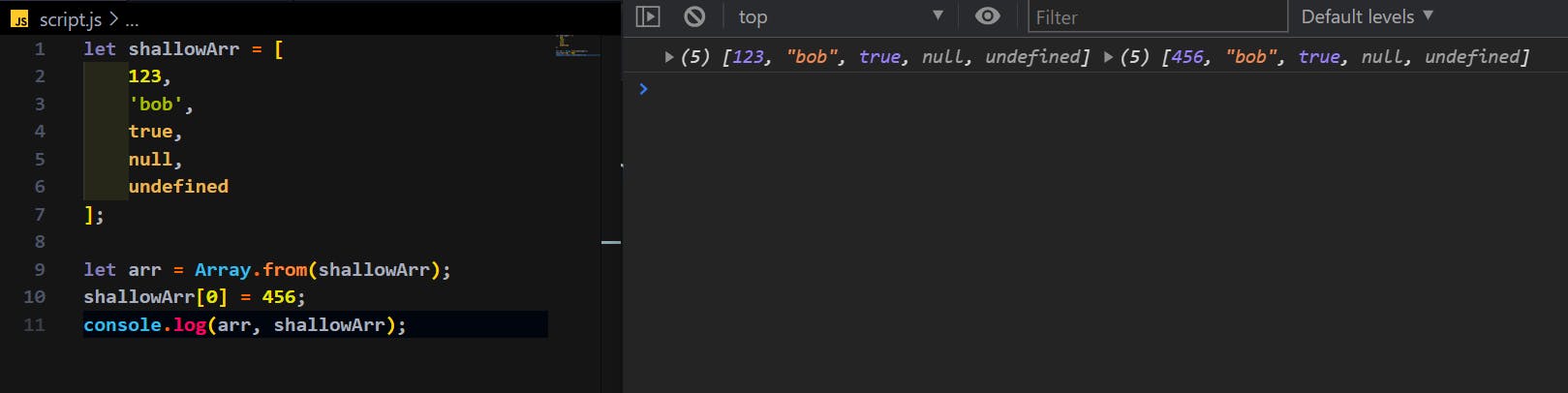
See, now as we have used one of the shallow copy methods, at line let arr = Array.from(shallowArr);, the shallowArr is actually copied to arr and not the reference of it as before.
Now that we understood what Shallow Copying is, on what kind of values we can do Shallow Copying and what are the useful methods.
Lets climb another step and try to under stand what Deep Copy means.
Deep Copy
Consider we have another new array deepArray like this:
let deepArr = [
123,
'bob',
true,
['Hank', 'Brent', 'Lacy'],
{
'Rouleau': 'Dog River',
'Wilcox': 'Woolerton'
}
];
If you see deepArr is having non-primitive values. It has a nested array, and a nested Object as well. Unlike the previous array we took as example, this array did not have all primitive values in it. So, exactly in this kind of scenario, if we want to create a new copy of the deepArr, shallow copying will no longer work.
Because, if you can see the above array, it has first 3 values as primitive values, but the 4th value, ['Hank', 'Brent', 'Lacy'], is a non-primitive value. So, if we try to do something like Array.from(deepArr);, the first 3 values of deepArr will be copied, but for the 4th and 5th values, its reference will be saved instead of values directly.
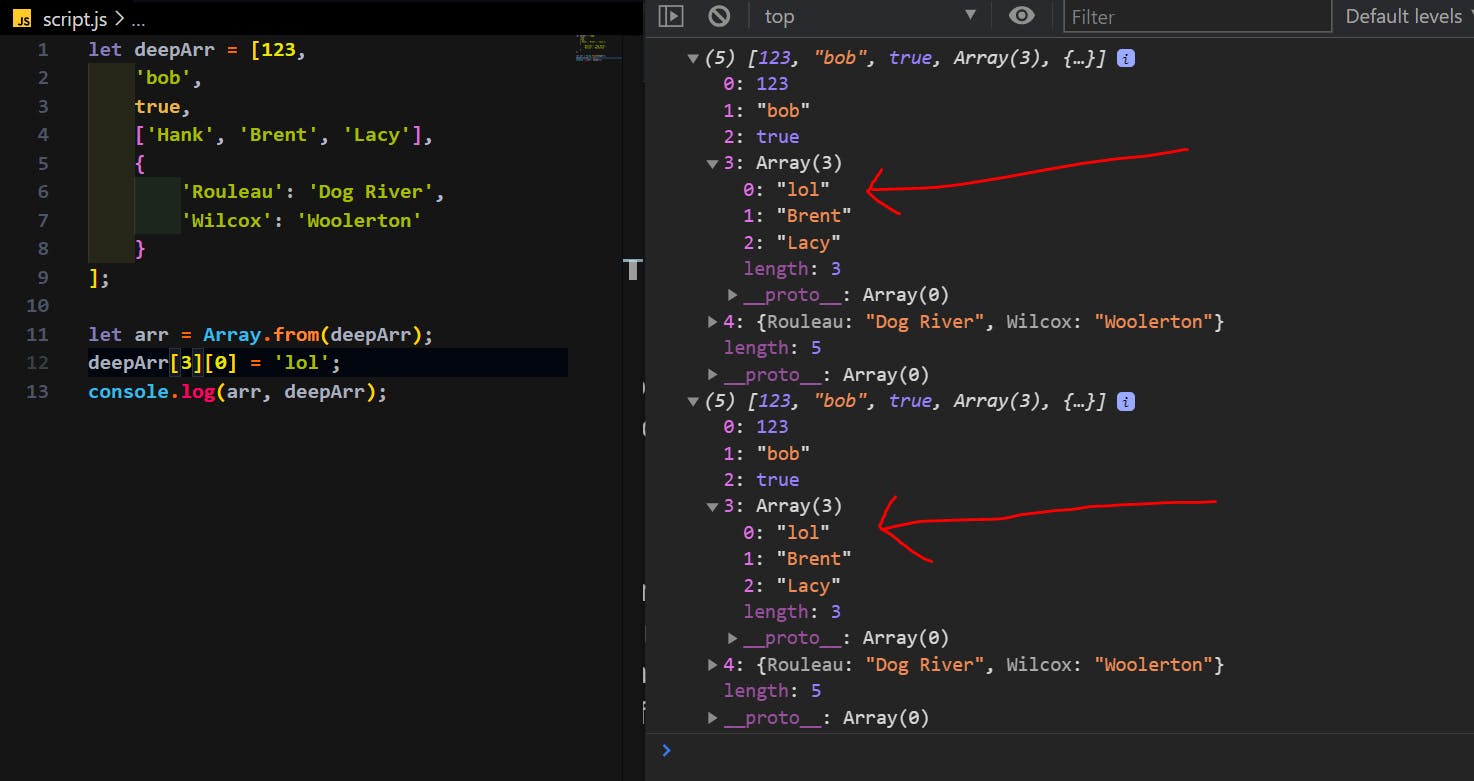
So, here if you can see, I tried to change the 0th value of the nested array (3rd value) of deepArr. But, as you can see, we faced the same issue as before. As I said, the remaining primitive values of the array are copied, but the non-primitive value is copied as a reverence.
So, in order to copy all the sub non-primitive values of a non-primitive value such as 'deepArr', we need to use a copying technique called Deep Copying.
In order to do Deep Copying, we need to use some set of methods:
/***********************
Deep Copy methods
1. JSON.parse(JSON.stringify())
2. Service Workers postMessage() onmessage
3. History API history.pushState(obj, title) history.state
4. Notification API new Notification("title", {data: obj} ).data
5. Build a custom recursive function
***********************/
Now, I will demonstrate you one of my favorite of all, that is JSON.parse(JSON.stringify()).
Basically what it will do is, convert the entire value to a string, and then again parse that string to convert into a new copy of it.
Let us see how that works:
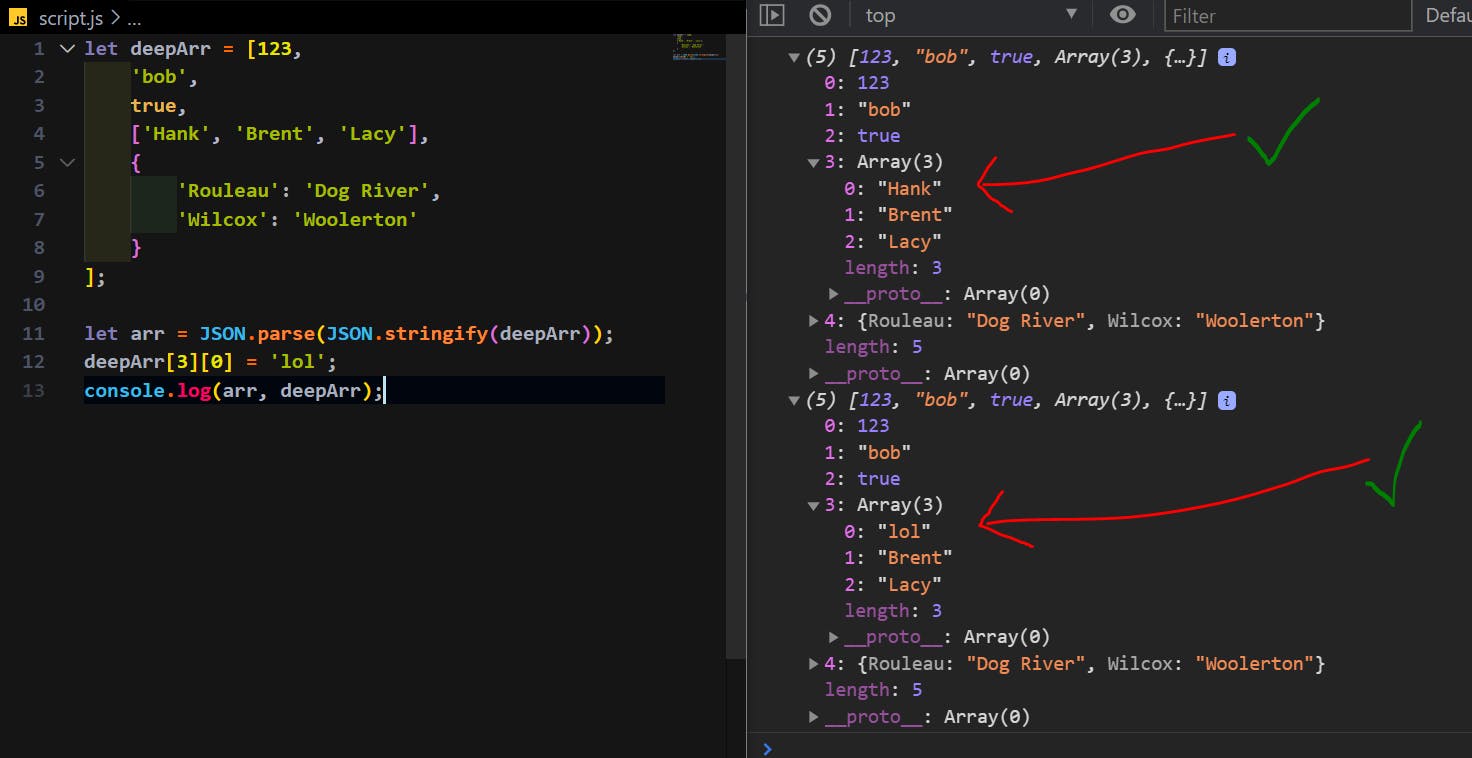
Now that you can see in the above picture, we have successfully copied the entire deepArr object including its non-primitive nested array values.
Conslusion
So, the conclusion is, there is a small difference in Shallow and Deep copying. Shallow copy is used to copy an non-primitive value such as array/object, which has all values of primitive type (such as 'shallowArr). But Deep Copy is also used to copy an non-primitive value such as array/object which has non-primitive values in it such as nested array/object (such as 'deepArr).
We came to an end of this long article. Hope you learned something today.